In this post, I will show you how to set up a secure FTP server on a Linux server with SSL/TLS encryption, using either a purchased SSL certificate or a Let’s Encrypt certificate.
Prerequisites:
- A Linux server with root access
- A domain name (e.g., ftp.example.com) pointed to your server IP address (Optional)
Table of Contents:
- Step 1: Install vsftpd
- Step 2: Configure vsftpd
- Step 3: Create FTP User Accounts
- Step 4: Configure Firewall
- Step 5: Test FTP Server
- Step 6: Enable SSL/TLS Encryption (Optional)
- Step 7: Test FTP Server with SSL/TLS Encryption
- Conclusion
Step 1: Install vsftpd
The first step is to install vsftpd, a popular FTP server software, on your Linux server. Open a terminal and run:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install vsftpd -yStep 2: Configure vsftpd
You need to configure it by editing the vsftpd configuration file /etc/vsftpd.conf. Open the file with a text editor, such as nano:
sudo nano /etc/vsftpd.confAdvertisements
Make the following changes to the configuration file:
anonymous_enable=NO
local_enable=YES
write_enable=YES
chroot_local_user=YES
Save the changes and close the file.
echo allow_writeable_chroot=YES >> /etc/vsftpd.conf && systemctl restart vsftpd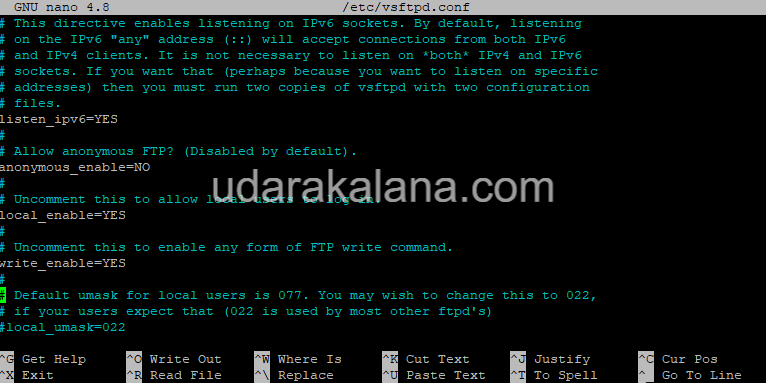
Step 3: Create FTP User Accounts
Next, you need to create FTP user accounts to allow users to connect to your FTP server. You can create local system users and set their passwords using the following command:
sudo useradd -m [username]
sudo passwd [username]Replace [username] with the name for the FTP user.
Step 4: Configure Firewall
If you have a firewall enabled on your Linux server, you need to configure it to allow FTP traffic. By default, FTP uses two ports for communication – port 20 and port 21. You need to open these ports in your firewall to allow FTP traffic. You can do this using a tool like UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) by running the following commands:
sudo ufw allow 20/tcp
sudo ufw allow 21/tcpStep 5: Test FTP Server
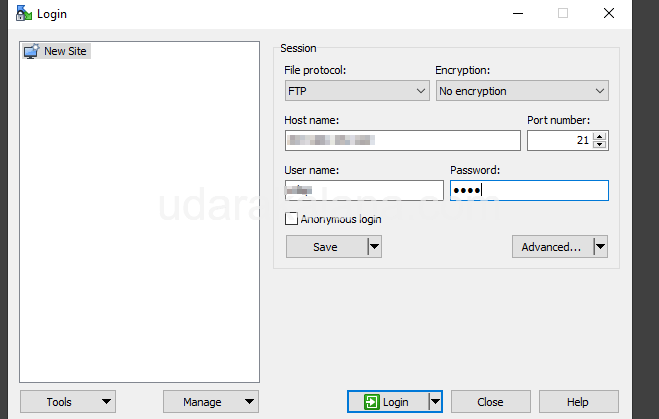
Once you have completed the above steps, your FTP server should be up and running. You can now test the FTP server by connecting to it using an FTP client such as Winscp. Enter the hostname or IP address of your Linux server, along with the FTP username and password that you created earlier. If everything is configured correctly, you should be able to connect and transfer files from your server.
Step 6: Enable SSL/TLS Encryption (Optional)
To secure your FTP server, you can enable SSL/TLS encryption. This step is optional, but highly recommended for the security of your FTP server.
Option A: Using a Purchased SSL Certificate
If you have already purchased an SSL certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), you can install it on your server. Here are the steps.
Step 6 A.1: Upload SSL Certificate Files
Upload the SSL certificate files (e.g., .crt and .key files) to a directory on your server, such as /etc/ssl/private/. You can use FTP or SCP to upload the files.
Step 6 A.2: Configure vsftpd for SSL/TLS
In the vsftpd configuration file /etc/vsftpd.conf, add the following lines or uncomment them if they already exist:
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/private/[your_domain_name].crt
rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/[your_domain_name].key
ssl_enable=YES
force_local_data_ssl=YES
force_local_logins_ssl=YESReplace [your_domain_name] with your actual domain name and the SSL certificate file location.
Step 6 A.3: Restart vsftpd Service
After making changes to the vsftpd configuration file, restart the vsftpd service for the changes to take effect:
sudo service vsftpd restartOption B: Using Let’s Encrypt Certificate
If you prefer to use a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt, you can install Certbot Here are the steps
Step 6 B.1: Install Certbot
Install Certbot on your server:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install certbot -yStep 6 B.2: Get Let’s Encrypt Certificate
Get a Let’s Encrypt certificate for your domain:
sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d ftp.example.comReplace ftp.example.com with your actual domain name.
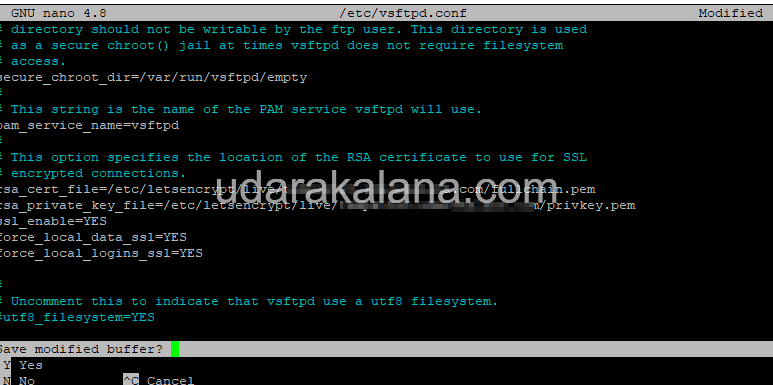
Step 6 B.3: Configure vsftpd for SSL/TLS
In the vsftpd configuration file /etc/vsftpd.conf, add the following lines:
rsa_cert_file=/etc/letsencrypt/live/ftp.example.com/fullchain.pem
rsa_private_key_file=/etc/letsencrypt/live/ftp.example.com/privkey.pem
ssl_enable=YES
force_local_data_ssl=YES
force_local_logins_ssl=YESAdvertisements
Replace ftp.example.com with your actual domain name.
Step 6 B.4: Restart vsftpd Service
After Generating the Let’s Encrypt certificate and making changes to the vsftpd configuration file, restart the vsftpd service:
sudo service vsftpd restart
Step 7: Test FTP Server with SSL/TLS Encryption
Test your FTP server with SSL/TLS encryption by connecting to it using an FTP client that supports SSL/TLS, Connect to your FTP server using the domain name, and choose the “TLS/SSL Explicit encryption” option in your FTP client.
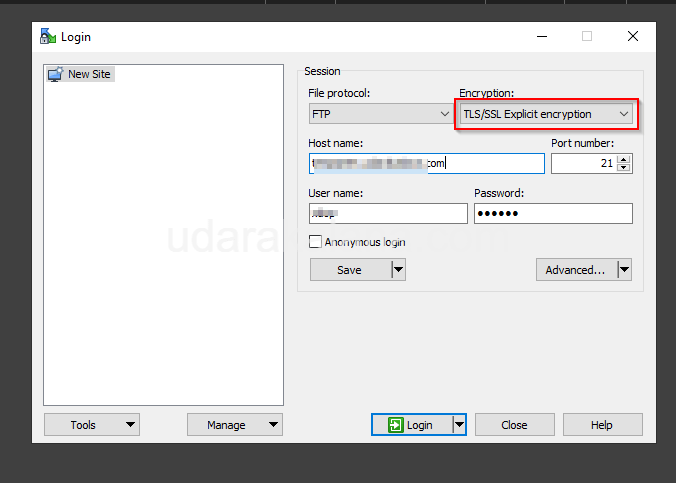
Conclusion
You have successfully set up a secure FTP server on your Linux server with SSL/TLS encryption. By enabling SSL/TLS encryption, you have added an additional layer of security to protect your file transfers.




thanks dude